What Is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) and Why It Matters in 2026

TL;DR
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the practice of optimizing content for AI-powered answer engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews. Unlike traditional SEO that focuses on rankings and clicks, GEO prioritizes AI comprehension, semantic clarity, and citation-ready content. As AI Overviews now appear in 49% of search results and LLM traffic continues rising, businesses must adapt their content strategy. Key tactics include structuring content in semantic chunks, implementing advanced schema markup, building authority through brand mentions and co-citations, and creating comprehensive articles with unique data. Start tracking your visibility across AI platforms now and optimize high-priority pages first to maintain competitive advantage in this rapidly evolving search landscape.
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) represents a fundamental shift in how content reaches audiences. It’s the practice of optimizing your digital content so AI-powered answer engines—ChatGPT, Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, Claude, and similar platforms—can understand, extract, and cite your information when responding to user queries. Unlike traditional search where users click through to websites, these generative engines synthesize information from multiple sources and present direct answers, often keeping users within the AI interface.
The stakes are significant. As of May 2025, AI Overviews appear in 49% of Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs), reflecting this evolution. With 60% of Google searches in 2024 keeping users on the search engine results page (SERP), it becomes crucial to develop strategies that captivate and engage audiences directly within these AI-enhanced environments. Businesses that fail to optimize for these AI systems risk becoming invisible in the primary way users now discover information. Early adopters gain a critical visibility advantage as the ecosystem matures and competition intensifies.
How GEO Differs from Traditional SEO (And Why Both Still Matter)
Traditional SEO optimizes for search engine rankings, click-through rates, and organic traffic. Success metrics focus on keyword positions, domain authority, and website visits. The goal is getting users to click your link among ten blue results on a search page.
GEO operates differently. Its primary focus is AI comprehension, information extraction, and citation worthiness. Success means your content appears in synthesized answers, gets quoted with attribution, or influences AI-generated recommendations—even when users never visit your website. GEO prioritizes semantic clarity over keyword density, values modular content structure over traditional page hierarchy, and emphasizes being citation-ready with clear, factual statements.
Despite these differences, GEO builds directly on SEO fundamentals. Technical accessibility remains essential—AI crawlers still need to access and render your content. E-E-A-T principles (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) matter even more for AI systems evaluating source credibility. Quality backlinks, clean site architecture, and mobile optimization all contribute to GEO success. The critical distinction is that GEO extends these foundations with AI-specific requirements: semantic chunking for embedding models, entity disambiguation for knowledge graphs, and multi-platform brand visibility beyond Google’s ecosystem.
Both approaches remain necessary. Traditional SEO still drives direct traffic and conversions. GEO ensures brand visibility and authority in the AI-mediated discovery layer that increasingly sits between users and websites. Neglecting either means missing opportunities in today’s hybrid search landscape.
The Core Principles of GEO: Writing Content AI Systems Can Understand and Quote
AI systems process content fundamentally differently than human readers or traditional search algorithms. Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on embedding models that convert text into mathematical representations, then retrieve relevant information through similarity matching. For your content to surface in AI-generated answers, it must be structured in ways these systems can efficiently parse, understand, and extract.
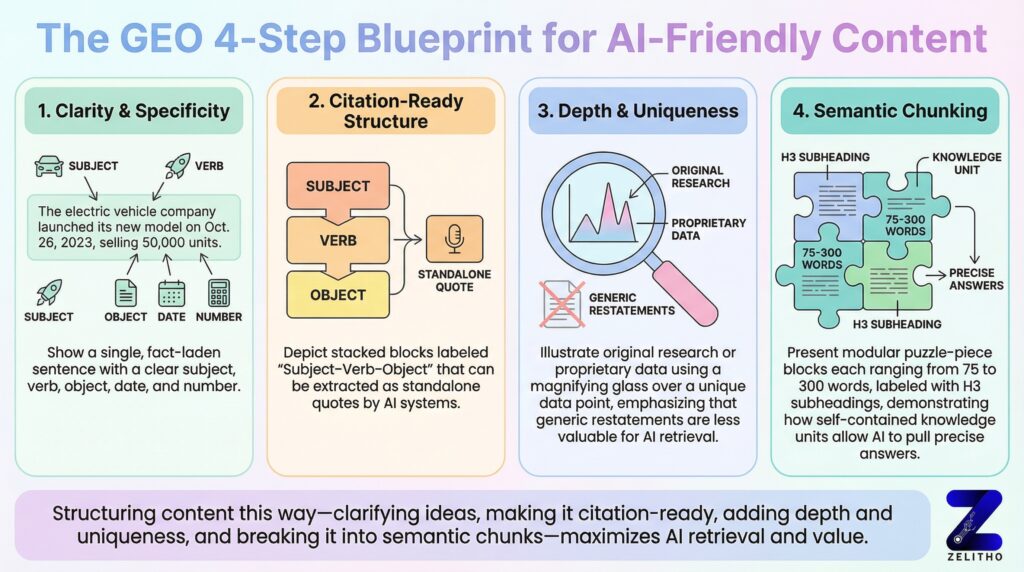
The foundation starts with clarity and specificity. Every paragraph should convey one clear idea with explicit context. Ambiguous references, lengthy tangents, and vague statements reduce extraction likelihood. AI systems favor content that states facts directly, provides specific numbers and dates, and connects concepts through explicit relationships rather than implied connections.
Citation-readiness is equally critical. AI platforms increasingly attribute sources, especially for factual claims. Content structured as quotable statements—with clear subject-verb-object construction and standalone context—gets cited more frequently. This means writing in a way that allows AI to extract a single sentence or paragraph that remains meaningful without surrounding text.
Factual depth and unique insights significantly increase retrieval probability. Generic content that restates widely available information holds little value for AI systems. Original research, proprietary data, expert commentary, and distinctive perspectives make your content irreplaceable and citation-worthy. When AI systems evaluate multiple sources, depth and uniqueness become primary differentiators.
Structure Content in Semantic Units (Chunks AI Can Extract)
Semantic chunking breaks content into discrete, focused sections that each answer a specific question or explain a distinct concept. These chunks typically range from 75 to 300 words—large enough to provide complete context but small enough for efficient processing by Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems and embedding models.
Think of each chunk as a self-contained knowledge unit. It should have a clear topic, provide relevant context, state key facts or concepts, and reach a logical conclusion—all without requiring readers to reference other sections. This modularity allows AI systems to extract and present individual chunks as complete answers, increasing your content’s utility and citation potential.
Practical implementation involves using descriptive subheadings, maintaining one main idea per paragraph, and creating explicit transitions between concepts. Each H3 section should address a discrete subtopic. Paragraphs within sections should follow clear logic: introduce the point, provide supporting details, offer an example or application. Avoid sprawling paragraphs that blend multiple concepts or require extensive context from earlier sections.
Use Entity Co-Occurrence and Disambiguation to Reduce Ambiguity
Entities—people, organizations, products, concepts, locations—form the foundation of how AI systems understand content relationships. Entity co-occurrence means mentioning related entities together to establish clear contextual connections. When you write about “machine learning,” explicitly mentioning “neural networks,” “training data,” and “predictive models” helps AI systems understand the specific context and relationships.
Disambiguation prevents confusion when terms have multiple meanings. “Apple” could reference fruit, a technology company, or a record label. Clear disambiguation involves providing enough context: “Apple Inc.,” “Granny Smith apples,” or “Apple Records.” Using structured data markup (especially Organization, Person, and Product schema) reinforces these distinctions programmatically.
For complex topics, define specialized terms on first use and connect them to established knowledge. If discussing “semantic search,” explicitly relate it to “natural language processing” and “vector databases.” This entity co-occurrence creates a semantic web that AI systems follow to understand your content’s place within broader topics. The more precisely you map entity relationships, the more accurately AI platforms can retrieve and cite your content in relevant contexts.
Practical GEO Optimization Techniques: A Step-by-Step Action Plan
Effective GEO implementation requires specific, actionable techniques that make your content AI-accessible and citation-worthy. These tactics build on content structure principles to create tangible optimization improvements.
Start with comprehensive content depth. Target 1,500+ words for substantive topics, but prioritize quality and focus over arbitrary length. Longer content allows thorough topic coverage, inclusion of supporting data, multiple entry points for different query types, and natural integration of related concepts—all factors that increase AI retrieval likelihood.
Optimize page titles and headings for natural language queries. AI systems process conversational questions, so titles like “How to Optimize Content for ChatGPT” perform better than “ChatGPT Content Tips.” Use question-based H2s where appropriate: “What Makes Content Citation-Worthy?” rather than “Citation Factors.”
Implement topic clustering through strategic internal linking. Create pillar pages on core topics and connect them to detailed subtopic pages. This architecture helps AI systems understand your content hierarchy and subject matter expertise. Each cluster becomes a knowledge hub that AI can reference comprehensively.
Enhance scannability through formatting. Use bullet points for lists, bold text for key facts and definitions, numbered steps for processes, and short paragraphs (3-4 sentences maximum). These formatting choices serve both human readers and AI parsing systems, making content extraction more efficient.
Optimize for voice search and conversational queries. Include natural question phrases in your content that match how people ask AI systems for information. Answer these questions directly and concisely within 2-3 sentences, then expand with additional detail. This structure supports both featured snippet extraction and AI-generated responses.
Write Comprehensive, In-Depth Content with Unique Data and Insights
Depth and originality are primary differentiators for AI citation selection. Generic content gets ignored; unique, authoritative content gets repeatedly referenced. Aim for articles of 1,500 words or more that thoroughly explore topics with original angles, proprietary data, expert interviews, or detailed case studies.
Original research holds exceptional value. Conduct surveys, analyze industry data, or compile original statistics. When you publish unique numbers, AI systems have no alternative sources—increasing citation probability substantially. Even small-scale research (customer surveys, internal data analysis) provides quotable, original information.
Include direct quotes from subject matter experts. Interview industry leaders, customers, or internal specialists. These quotes add authority, provide unique perspectives, and create citation-ready statements. Attribute quotes clearly with names, titles, and organizations to enhance credibility.
Support claims with specific, recent data. Cite statistics, include publication dates, and reference authoritative sources. When using third-party data, synthesize insights rather than simply restating facts. Your analysis and interpretation become the unique, citation-worthy elements.
Implement Advanced Structured Data Beyond Basic Schema.org
Basic schema markup (Article, Organization, FAQPage) provides foundational AI accessibility. Advanced implementation creates a comprehensive content graph that significantly improves AI comprehension and retrieval accuracy.
Deploy specialized schema types relevant to your content. Use HowTo schema for instructional content, Recipe schema for food content, Product schema for commercial pages, and Event schema for time-specific content. Each schema type provides structured signals that help AI systems categorize and extract information precisely.
Create internal knowledge graphs that connect related entities across your site. Tag articles with consistent entity identifiers, implement breadcrumb schema showing content relationships, and use SameAs properties to connect your entities to established knowledge bases like Wikidata. This semantic linking helps AI systems understand your content ecosystem holistically.
Consider custom ontologies for specialized industries. If standard schema doesn’t capture your domain specifics, create structured metadata systems that define entity types, relationships, and attributes relevant to your field. While AI systems may not directly consume custom ontologies, the structural discipline improves content clarity and organization—indirectly benefiting AI comprehension.
However, presently, AI crawlers encounter several challenges, with 34% of requests ending in errors such as 404. Ensure your structured data is error-free, pages are accessible, and your robots.txt doesn’t inadvertently block AI crawlers. Notably, only Google’s Gemini and AppleBot can process JavaScript, emphasizing the need to optimize websites’ technical foundations. If your site relies heavily on JavaScript rendering, implement server-side rendering or static HTML alternatives for critical content.
Building Authority and Trust for AI Systems: E-E-A-T, Brand Mentions, and Co-Citations
Authority signals influence whether AI systems select your content as a trusted source. These signals extend beyond traditional backlinks to encompass brand visibility, entity associations, and cross-platform presence.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) remains foundational. Establish clear author credentials with detailed bios, professional affiliations, and subject matter expertise. Link authors to their social profiles, publications, and credentials. For organizational content, prominently display company background, certifications, industry recognition, and trust indicators.
Brand mentions—even unlinked ones—significantly impact AI perception of authority. When your brand appears frequently across the web in relevant contexts, AI systems infer legitimacy and relevance. Build mentions through strategic PR, expert commentary in industry publications, guest posts on authoritative sites, participation in industry directories, and active engagement on platforms like LinkedIn, Reddit, and industry forums.
Co-citations establish contextual relevance. When your brand appears alongside competitors or industry leaders in discussions, comparisons, and roundups, AI systems learn your relative position and topical associations. Seek inclusion in “best of” lists, comparison articles, and industry trend pieces. Contribute to discussions where your competitors are mentioned, positioning your brand within the same knowledge space.
Earn backlinks from high-authority domains in your industry. Quality matters substantially more than quantity. A single mention in an authoritative industry publication carries more weight than dozens of low-quality directory listings. Focus on earning citations from sources AI systems already recognize as trustworthy.
Expand beyond Google-centric SEO to build multi-platform presence. AI systems increasingly train on diverse data sources including Reddit discussions, YouTube transcripts, LinkedIn posts, academic papers, and industry forums. Active, valuable participation across these platforms creates distributed authority signals that reinforce your expertise across AI training data and retrieval systems.
Tracking and Measuring Your GEO Performance Across AI Platforms
GEO measurement requires different approaches than traditional SEO analytics. You’re tracking visibility within AI-generated responses rather than ranking positions and click-through rates.
Start with manual testing across major AI platforms. Monthly, query ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Google AI Overviews, and Bing Chat with your brand name, key product names, and category queries where you want visibility. Document whether you appear, how you’re described, context of mentions, and citation presence. Track changes over time to identify visibility trends.
Develop a standardized query set that includes branded searches, category queries, comparison questions, and how-to questions relevant to your business. Test each query across multiple platforms and record results systematically. This baseline tracking reveals which content types and topics generate citations and where visibility gaps exist.
Monitor referral traffic from AI platforms in Google Analytics. Configure tracking to identify visits from ChatGPT, Perplexity, and other AI tools. Analyze which content receives AI-driven traffic, user behavior patterns from these sources, and conversion rates compared to traditional search traffic. This data validates which GEO tactics drive measurable business impact.
For enterprise-scale tracking, use dedicated GEO monitoring tools. Platforms like Semrush Enterprise AIO track brand visibility across LLMs, monitor citations and source attributions, analyze competitor presence in AI responses, and provide visibility trend reports. These tools automate what would otherwise require extensive manual testing.
Track brand mentions across the broader web using tools like Google Alerts, Mention, or Brand24. Since unlinked mentions influence AI authority signals, monitoring where and how your brand appears contextually informs your authority-building strategy.
Establish baseline metrics now. LLM traffic continues growing rapidly, and early tracking data becomes invaluable for measuring improvement and identifying optimization opportunities. Start simple with monthly manual checks, then expand to automated tools as resources allow.
Preparing for Agentic Search: The Future of AI-Driven Discovery
Agentic AI represents the next evolution beyond answer engines. These systems act as autonomous agents that research topics, compare options, make recommendations, and complete tasks on behalf of users—often without users visiting websites at all.
Imagine a user asking their AI agent: “Find the best project management software for my 15-person remote team under $2,000 annually.” The agent doesn’t present search results. It researches options, compares features and pricing, reads reviews, evaluates fit for the specific use case, and presents a curated recommendation with reasoning—all autonomously.
For content creators and businesses, this shift has profound implications. Your content must be clear enough for AI agents to accurately extract and synthesize, trustworthy enough for AI systems to recommend with confidence, and distributed widely enough to appear across the information ecosystem agents consult. Traditional website traffic becomes less relevant; being part of the knowledge foundation AI agents rely on becomes critical.
Future-proof your GEO strategy by embedding your brand in the broader knowledge graph. This means earning mentions and citations across diverse platforms, participating actively in industry communities where knowledge is created and shared, contributing expert perspectives that agents can reference, and maintaining consistent, accurate brand information across the entire web.
Build relationships with platforms and publications that AI systems trust. Contribute thought leadership to industry publications, participate in expert panels and podcasts, engage meaningfully in professional communities, and create original research that becomes reference material. These activities ensure your expertise is woven into the knowledge fabric AI agents consult.
Prepare for a world where direct user interactions decrease but brand authority and knowledge contribution matter more than ever. The content that shapes AI understanding and recommendations will come from recognized experts and trusted brands. Position yourself accordingly through consistent expertise demonstration and knowledge sharing across multiple platforms and formats.
Frequently Asked Questions
GEO focuses on optimizing content for AI-powered answer engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews that synthesize and cite information, while SEO targets traditional search rankings and click-throughs. GEO requires semantic clarity, modular structure, and citation-ready content. Both share core principles like E-E-A-T and technical accessibility, but GEO prioritizes AI comprehension over keyword density and values being quoted or cited over receiving clicks.
Break content into short, focused sections of 75-300 words that each answer a single question. Use clear headings, one idea per paragraph, bullet points, and bold text for key facts. Write statements that can stand alone without surrounding context. Add schema markup including FAQPage and HowTo types. Ensure your site isn’t JavaScript-heavy and doesn’t block AI crawlers in robots.txt, as only Google’s Gemini and AppleBot can currently process JavaScript effectively.
Start with manual testing by querying ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, and Claude monthly with your brand and category terms. Document when and how you appear in responses. Monitor referral traffic from AI platforms in Google Analytics under acquisition sources. For automated tracking, use tools like Semrush Enterprise AIO, which tracks visibility across LLMs and provides citation reports. Combine these approaches for comprehensive performance monitoring.
AI systems evaluate authority by analyzing brand mentions across the web, including unlinked references. Co-citations—being mentioned alongside competitors or authoritative entities—help LLMs understand your relevance and context within your industry. These signals build your position in the knowledge graph AI systems consult when generating responses. Build mentions through PR, guest posts, industry directories, and active participation on platforms like Reddit and LinkedIn where AI training data is sourced.
Start Optimizing for GEO Today to Stay Visible in AI-Driven Search
The transition to AI-mediated search is accelerating, not slowing. With AI Overviews already appearing in nearly half of all search results and the majority of searches keeping users on the results page rather than sending clicks to websites, the urgency for GEO adoption is clear. Businesses that optimize now gain significant visibility advantages as competition intensifies and the ecosystem matures.
Begin with your highest-priority pages: core product and service pages, top-performing blog content, and pages targeting high-intent keywords. Apply the principles outlined here: structure content in semantic chunks, implement comprehensive schema markup, build authority through strategic brand mentions and co-citations, and create comprehensive articles with unique data and expert insights. Track your visibility across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews monthly to measure progress and identify opportunities.
GEO is not a replacement for traditional SEO but an essential complement. Continue optimizing for search rankings and click-through rates while simultaneously ensuring your content is accessible, comprehensible, and citation-worthy for AI systems. This dual approach maintains visibility across both traditional and AI-mediated discovery channels.
The future belongs to brands that successfully position themselves as trusted knowledge sources across the distributed ecosystem of AI platforms, answer engines, and agentic systems. Start today by auditing your existing content for GEO readiness, implementing the practical techniques outlined above, and establishing consistent tracking processes. Early adopters in your industry will define the standards and capture the visibility advantages as GEO becomes standard practice across all digital content strategies.