E-E-A-T SEO Strategy: How to Build Trust and Authority in the Age of AI Content

TL; DR
- In today’s AI-saturated content landscape, ranking on Google requires more than keyword optimization—it demands genuine trust, expertise, and authority.
- This comprehensive guide explores Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness) and provides eight actionable strategies to build credibility with AI-assisted content.
- You’ll learn why E-E-A-T matters more than ever, how AI search is reshaping content discovery, and proven tactics to demonstrate first-hand experience, cite credible sources, showcase author credentials, and optimize for niche audiences.
- Whether you’re creating human-written or AI-assisted content, mastering E-E-A-T is your competitive advantage for ranking higher and earning lasting reader trust in the age of AI content.
AI has fundamentally changed how content is created, but it hasn’t changed what readers and search engines value most: credibility. As generative AI tools flood the internet with generic articles, Google’s E-E-A-T framework has become the critical differentiator between content that ranks and content that disappears. This guide will show you exactly how to apply E-E-A-T principles to your content strategy – whether you’re writing entirely by hand, using AI assistance, or combining both approaches.
What Is E-E-A-T in SEO and Why Does It Matter More Than Ever?
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness—a framework Google’s quality raters use to evaluate content credibility. While not a direct ranking factor, E-E-A-T influences how Google’s algorithms assess content quality, especially for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics like health, finance, and legal advice1. In the AI content era, demonstrating E-E-A-T is critical to differentiate your content from generic, automated outputs.
Think of E-E-A-T as Google’s answer to a fundamental question: “Why should we trust this content?” When millions of AI-generated articles compete for the same keywords, search engines must identify which sources genuinely serve users. E-E-A-T provides the evaluation criteria that separates valuable content from noise.
The Evolution From E-A-T to E-E-A-T: Why Experience Was Added
In December 2022, Google added the first ‘E’ for Experience to emphasize that first-hand knowledge significantly enhances content value2. This update reflects Google’s push for authentic, lived expertise over purely academic or AI-generated content.
The addition of Experience wasn’t arbitrary. Google recognized that someone who has actually used a product, implemented a strategy, or lived through a situation provides insights no amount of research alone can replicate. A financial advisor who has personally navigated market volatility offers different value than an AI summarizing investment theory. This distinction becomes crucial as AI tools become more sophisticated at mimicking expertise without possessing actual experience.
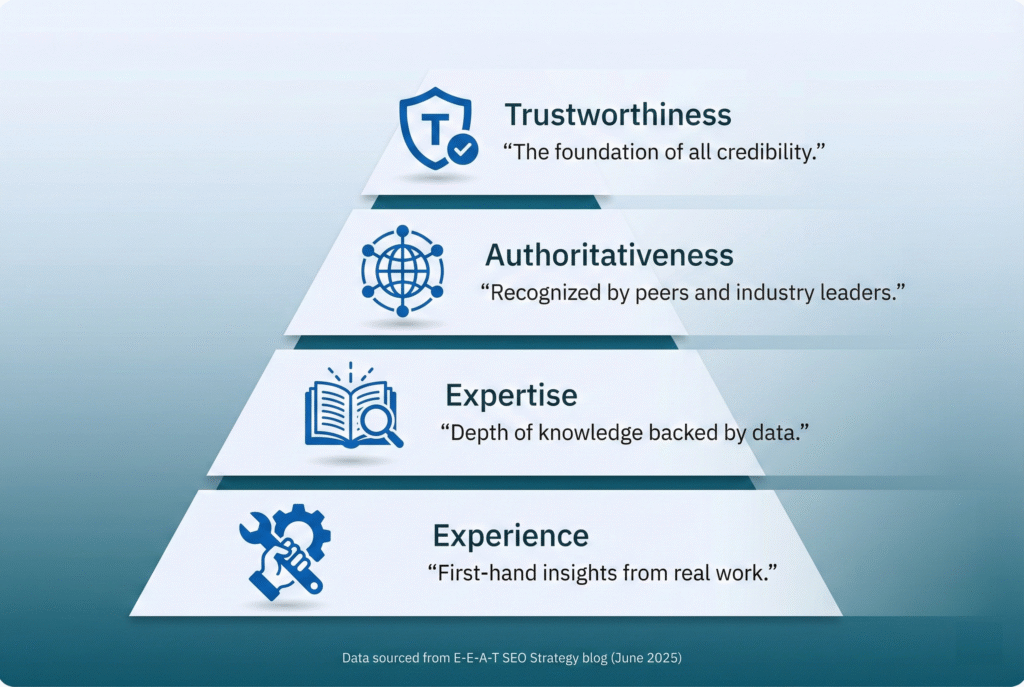
Understanding the Four Pillars of E-E-A-T
Each component of E-E-A-T serves a specific purpose in establishing content credibility. Experience represents first-hand knowledge—the practical, lived understanding that comes from direct interaction with a topic. Expertise reflects depth of subject mastery, typically demonstrated through education, training, or extensive study. Authoritativeness indicates industry recognition, such as citations by other experts, media mentions, or professional credentials.
Trustworthiness serves as the foundation that ties the other three pillars together3. You can possess experience, expertise, and authority, but without trust—demonstrated through accuracy, transparency, and ethical practices—your content loses its power to influence and rank. Trust encompasses everything from citing sources correctly to acknowledging limitations in your knowledge.
Why E-E-A-T Is Not a Direct Ranking Factor (But Still Critical)
E-E-A-T itself isn’t a ranking signal that Google’s algorithms directly measure. However, Google uses a mix of factors that identify content with strong E-E-A-T characteristics. The framework appears over 120 times in Google’s Search Quality Rater Guidelines4, which train human raters to evaluate content quality and inform future algorithm updates.
This distinction matters. Google cannot directly measure “expertise” or “trust” through code alone. Instead, the algorithm looks for signals correlated with these qualities: author credentials displayed prominently, links from authoritative sites, accurate information verified against knowledge graphs, positive user engagement metrics, and content depth. When quality raters consistently score certain types of content highly for E-E-A-T, engineers use those patterns to refine ranking systems.
The AI Content Challenge: Why Trust and Authority Are Under Threat
AI tools like ChatGPT and Google Gemini have democratized content creation, but they’ve also flooded the internet with generic, potentially inaccurate content. These tools can produce coherent, grammatically correct text at scale, but they lack genuine understanding, cannot verify facts in real-time, and sometimes generate plausible-sounding misinformation called “hallucinations.” Without human oversight, AI-generated content often misses emotional resonance, contextual nuance, and the first-hand insights that readers value most.
The credibility gap emerges from AI’s fundamental limitations. Large language models predict probable word sequences based on training data—they don’t “know” anything in the way humans do. When an AI writes about implementing a marketing strategy, it’s synthesizing patterns from thousands of articles, not drawing from actual campaign experience. This creates surface-level content that may answer questions technically while missing the depth, warnings, and contextual wisdom that come from lived expertise.
How AI Search Engines Are Changing User Behavior and Content Discovery
Search behavior is shifting from traditional link-based SERPs to AI-generated answers through Google’s AI Overviews, Bing Chat, and platforms like Perplexity. Users now often receive synthesized responses instead of ten blue links, fundamentally changing how content gets discovered. Brands increasingly compete for citations in AI summaries rather than top 10 rankings—a shift that makes E-E-A-T even more critical.
AI search engines prioritize sources they can confidently cite. When generating an overview, these systems assess source credibility using signals aligned with E-E-A-T: author credentials, domain authority, content accuracy, citation patterns, and user engagement. Content lacking these trust signals gets filtered out, while authoritative sources earn prominent placement and attribution. This means your E-E-A-T optimization directly impacts visibility in the AI-powered search landscape.
The Risk of Publishing Low-Quality AI Content
Recent data shows 71% of businesses now use generative AI for content creation5. However, publishing unchecked AI content carries significant risks: spreading misinformation, creating thin content that provides little user value, and potentially triggering ranking penalties under Google’s spam policies.
Google’s algorithms have evolved to detect patterns associated with low-quality automated content: repetitive phrasing, lack of original insights, missing source citations, shallow treatment of topics, and content that serves search engines rather than humans6. Sites that publish large volumes of AI content without substantial human review often experience ranking volatility or manual actions. The solution isn’t avoiding AI entirely—it’s ensuring human expertise validates, enriches, and adds genuine value to AI-assisted drafts.
The Five Levels of E-E-A-T: Where Does Your Content Stand?
Google’s Quality Rater Guidelines outline a five-tier system for assessing content quality: Lowest, Low, Medium, High, and Highest. Understanding these levels helps you objectively evaluate your content and identify improvement opportunities.
Lowest quality content deliberately harms users through scams, malicious downloads, or dangerous misinformation. It may also include completely inaccurate YMYL information or pages created solely to manipulate rankings. Low quality content shows minimal effort, lacks clear purpose, provides inadequate main content for the topic, or comes from sources with poor reputations. Think thin affiliate pages with no original value or articles with numerous factual errors.
Medium quality content achieves its stated purpose adequately but lacks the depth, originality, or expertise to stand out. The information is generally accurate but not particularly helpful beyond surface-level answers. Many AI-generated articles without human enhancement fall into this category.
High quality content demonstrates clear expertise, cites credible sources, provides comprehensive coverage of topics, and shows evidence of significant time and effort. Highest quality content represents the gold standard: original research, expert-level analysis, first-hand experience shared with exceptional depth, and content that users bookmark, share, and reference repeatedly. These pages often become the definitive resource in their niche.
8 Proven Strategies to Build E-E-A-T in the Age of AI Content
Building authentic trust and authority requires intentional strategy, not shortcuts. These eight research-backed tactics work whether your content is fully human-written, AI-assisted, or a hybrid approach. Each strategy addresses specific E-E-A-T components while creating cumulative credibility that elevates your entire content library.
1. Showcase Real Experience and First-Hand Insights
First-hand experience cannot be replicated by AI—it’s your strongest differentiator. Share personal stories, detailed case studies, original research, or behind-the-scenes processes that demonstrate you’ve actually done what you’re teaching2. Readers trust experiential content more than generic advice because it carries the weight of reality, including what didn’t work and why.
When using AI to assist with drafts, treat the output as a structural foundation. Add your unique perspective in specific, concrete ways: exact metrics from your campaigns, screenshots showing results, timestamps documenting your journey, or anecdotes revealing the human challenges behind successful outcomes. For example, instead of writing “email marketing can increase conversions,” share “When we A/B tested subject lines with personalization tokens, our open rate jumped from 18% to 31% within the healthcare segment—but the same approach failed with our B2B audience because decision-makers viewed it as automated spam.”
2. Build Expertise Through Data-Backed, Well-Researched Content
Support every significant claim with credible sources, current statistics, expert quotes, or peer-reviewed studies. This practice serves dual purposes: it validates your arguments and demonstrates research depth that AI alone cannot provide. Fact-checking AI outputs is non-negotiable—verify every statistic, confirm quotes against original sources, and ensure citations link to authoritative publications.
Layer multiple types of evidence throughout your content. Combine quantitative data with qualitative insights, industry reports with expert interviews, and historical context with emerging trends. For instance, when discussing AI content effectiveness, note that a meta-analysis of seven studies found AI-generated social media content elicited 11.6% higher user interaction than human-generated content5, while also explaining the methodology limitations and contextual factors affecting these results. This balanced approach builds expertise credibility.
3. Establish Authoritativeness With Visible Author Credentials
Create detailed author bios that showcase relevant qualifications, professional experience, and industry recognition. Link to professional profiles like LinkedIn, published works, speaking engagements, or media mentions. Display certifications, awards, or affiliations with respected organizations. Readers trust people more than faceless corporate brands, making personal branding a powerful authority amplifier.
Your author bio should answer three questions: Why should readers trust this person? What unique qualifications do they bring? How can readers verify their expertise? Include specifics: “Sarah Chen, VP of Digital Marketing with 12 years optimizing Fortune 500 brands, published researcher in the Journal of Digital Advertising, and regular speaker at Content Marketing World” carries far more weight than “marketing expert with years of experience.” Update bios regularly as credentials evolve, and ensure every article displays author information prominently.
4. Earn Trust Through Transparency, Accuracy, and Regular Updates
Transparency builds long-term reader loyalty more effectively than appearing perfect. Disclose AI use where applicable, correct errors publicly when discovered, cite sources clearly, and keep content current with updated statistics and evolving best practices. Acknowledge uncertainties rather than presenting everything as absolute truth—admitting “based on current data” or “in our experience” demonstrates intellectual honesty.
When you find an error, update the content and add a note: “Updated March 2025: Corrected conversion rate data from original study.” This transparency signals that accuracy matters more than ego. Similarly, if you’re testing an AI-assisted workflow, share both successes and failures honestly. Readers appreciate learning what didn’t work and why, because that context helps them avoid similar mistakes. Trust accumulates through consistent, demonstrated commitment to reader welfare over self-promotion.
5. Optimize for Niche Audiences, Not Generic Topics
Narrow your focus to specific pain points, industries, or user personas. Hyper-relevant content addressing precise needs outperforms broad, shallow articles targeting everyone. This specialization naturally demonstrates expertise because generalists cannot match the depth specialists provide in their domains.
Instead of writing “social media marketing tips,” target “Instagram Reels strategy for dermatology practices attracting patients aged 45-60.” This specificity forces deeper research, attracts a more engaged audience, and positions you as the expert for that exact use case. Niche content also faces less competition and often ranks more easily because fewer creators invest in such focused topics. AI tools work best when you provide detailed context about your target audience—use them to scale niche content creation while maintaining the specificity that establishes authority.
6. Build Backlinks From Industry-Respected Sources
Authoritative backlinks remain one of the strongest E-E-A-T signals. When respected industry publications, academic institutions, or established experts link to your content, they essentially vouch for your credibility. Focus on earning links through genuinely valuable content rather than manipulative link-building tactics.
Create linkable assets: original research reports, comprehensive guides, unique data visualizations, or tools that solve specific problems. Conduct expert roundups where you interview authorities and they naturally link when sharing their contributions. Contribute guest posts to reputable publications in your field, not for direct SEO value, but to build relationships and demonstrate expertise to wider audiences. Quality over quantity applies—one link from a recognized industry authority carries more E-E-A-T weight than hundreds of links from low-quality directories.
7. Demonstrate Topical Authority Through Comprehensive Content Clusters
Build topic clusters around your core expertise areas: pillar content covering broad topics comprehensively, supported by cluster content diving deep into specific subtopics. This structure signals topical authority by showing you’ve thoroughly covered a subject from multiple angles, not just written isolated articles targeting keywords.
For example, if establishing authority in “sustainable e-commerce,” create a pillar page covering the full landscape, then develop cluster content on sustainable packaging solutions, carbon-neutral shipping strategies, eco-friendly product sourcing, green payment processing, and consumer psychology around sustainability. Internally link these pieces strategically. This architecture helps both users and search engines understand your depth of coverage, while providing the comprehensive resource library that positions you as the go-to expert.
8. Monitor and Adapt Based on Performance Data and User Feedback
E-E-A-T optimization is not a one-time project—it requires ongoing monitoring and refinement. Track metrics beyond rankings: time on page, scroll depth, return visitor rates, and social sharing patterns reveal whether readers find your content trustworthy and valuable. Use tools like Google Search Console to identify which content earns featured snippets or AI Overview citations—these are strong E-E-A-T signals.
Actively solicit user feedback through comments, surveys, or direct outreach. Questions like “What information was missing?” or “What would make this more helpful?” often reveal gaps in expertise demonstration or trust signals. When multiple readers request clarification on the same point, that signals an opportunity to add depth. Similarly, if certain author bios generate more engagement or trust signals, analyze what works and apply those elements across your content team.
How to Audit Your Content for E-E-A-T Gaps
Regular content audits identify specific weaknesses undermining your E-E-A-T. Start by categorizing your content library: which pieces target YMYL topics requiring highest trust standards versus informational content with lower stakes. Apply Google’s five-tier quality framework to evaluate each piece objectively.
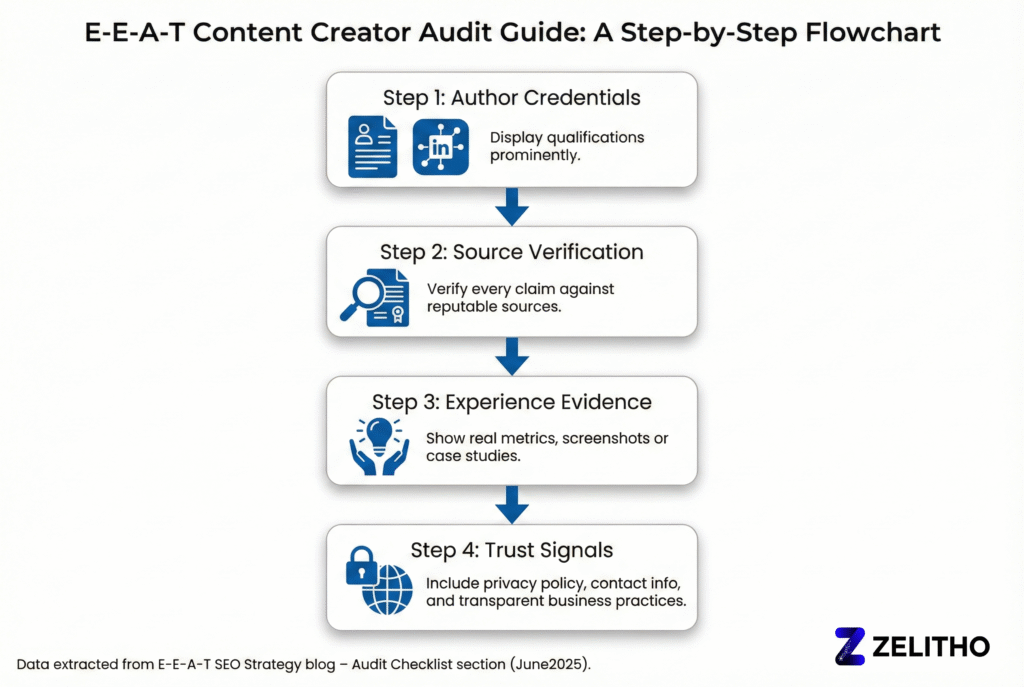
Create an E-E-A-T checklist for systematic evaluation: Does the author bio establish relevant credentials? Are all factual claims sourced from credible publications? Does the content demonstrate first-hand experience through specific examples? Is information current and recently updated? Do external authoritative sites link to this content? Are user engagement metrics healthy? Does the page include trust signals like contact information, privacy policies, and transparent business practices?
Prioritize improvements based on impact potential. High-traffic pages with medium E-E-A-T ratings offer quick wins—adding author credentials, updating statistics, or enriching with case studies can significantly boost their performance. YMYL content scoring low requires immediate attention due to higher risk. Use competitor analysis to understand the E-E-A-T bar in your niche—what credentials, sources, and depth do top-ranking competitors demonstrate?
The Future of E-E-A-T in an AI-First Search Landscape
As AI becomes more sophisticated at generating human-like content, E-E-A-T’s importance will intensify rather than diminish. Search engines and readers will demand stronger proof of genuine expertise, lived experience, and trustworthiness to cut through the noise. The brands that invest in building authentic authority now will command competitive advantages as AI content becomes ubiquitous.
Google has explicitly stated its focus on rewarding helpful content created for people, regardless of whether AI assists in production7. The key phrase is “helpful content created for people”—content must serve user needs first, demonstrate clear expertise, and provide value beyond what users could find through AI chatbots alone. AI should enhance your expertise and efficiency, not replace the human judgment, experience, and authority that readers trust.
Emerging trends point toward increasing integration of author reputation signals, real-time fact-checking against knowledge graphs, and stronger penalties for sites publishing misleading AI-generated content at scale. Forward-thinking content strategies will emphasize quality over quantity, depth over breadth, and authentic expertise over keyword optimization. Building genuine E-E-A-T isn’t a shortcut—it’s the sustainable path to lasting search visibility and reader trust.
Conclusion
E-E-A-T has evolved from an SEO concept to a fundamental content strategy requirement in the AI era. As generative AI democratizes content creation, the differentiator between ranking and obscurity is authentic expertise, first-hand experience, recognized authority, and demonstrated trustworthiness. Google’s algorithms increasingly reward content that serves readers first, backed by verifiable credentials and genuine subject matter depth.
The strategies outlined in this guide—showcasing real experience, citing credible sources, displaying author credentials, maintaining transparency, optimizing for niche audiences, earning quality backlinks, building content clusters, and monitoring performance—create a comprehensive framework for E-E-A-T excellence. Whether you write entirely by hand or use AI assistance, the principles remain constant: provide unique value that only your experience and expertise can deliver.
Start by auditing your existing content library for E-E-A-T gaps, prioritize improvements on high-value pages, and commit to the ongoing work of building genuine authority in your niche. The investment in E-E-A-T pays long-term dividends through sustainable rankings, reader loyalty, and competitive positioning that AI tools alone cannot replicate. In an increasingly AI-powered search landscape, trust and expertise aren’t just ranking factors—they’re your lasting competitive advantage.
FAQ
E-E-A-T stands for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. It’s a framework Google uses to evaluate content quality, especially for topics that could impact readers’ health, financial security, or safety. While not a direct ranking factor, E-E-A-T influences how algorithms assess content credibility.
AI-generated content isn’t inherently bad for E-E-A-T—it depends on how you use it. Content created entirely by AI without human expertise, fact-checking, or original insights typically lacks the experience and authority needed to rank well. However, AI-assisted content where experts use tools to enhance their writing, then add unique insights and verify accuracy, can demonstrate strong EEAT.
Share specific examples from your own work: case studies with real metrics, behind-the-scenes processes, lessons learned from failures, screenshots or documentation of results, and detailed explanations of how you implemented strategies. Avoid generic advice—the more specific and personal your insights, the stronger your experience demonstration.
Formal credentials help, especially for YMYL topics like medical or legal advice, but aren’t always required. You can demonstrate expertise through consistent, high-quality content over time, industry recognition, practical experience, and results you’ve achieved. Building a portfolio of authoritative content and earning links from respected sources establishes E-E-A-T even without formal degrees.
Update content whenever significant changes occur in your field, new research emerges, statistics become outdated, or user needs evolve. For evergreen content, review and refresh at least annually. For rapidly changing topics like technology or current events, quarterly or even monthly updates may be necessary to maintain trust and accuracy.
Sources:
1. https://searchengineland.com/guide/google-e-e-a-t-for-seo
2. https://www.searchenginejournal.com/google-e-e-a-t-how-to-demonstrate-first-hand-experience/474446/
3. https://foundationinc.co/learn/what-is-eeat-experience-expertise-authority-trust/
4. https://blog.clickpointsoftware.com/google-e-e-a-t
5. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959804925010007
6. https://developers.google.com/search/docs/fundamentals/creating-helpful-content
7. https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2023/02/google-search-and-ai-content