AI Agents in 2025: A Comprehensive Guide

TL;DR
AI agents, powered by advanced LLMs, are poised to revolutionize industries in 2025. This guide defines these autonomous systems, differentiates them from traditional bots, and explains their cognitive loop involving perception, memory, reasoning, and action. We explore key applications across sectors, delve into leading development platforms like Lyzr AI and LangChain, and detail essential strategies for monitoring AI agents, ensuring performance, data privacy, and ethical operation.
Explore the surging landscape of AI agents and LLMs in 2025.
This comprehensive guide covers what AI agents are, how they work, top development platforms, their applications, and essential strategies for effective monitoring and management.
Keywords AI: How to Monitor LLMs and AI Agents in 2025
The year 2025 marks a significant inflection point in artificial intelligence. We are moving beyond static AI models and witnessing the proliferation of dynamic, autonomous systems: AI agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). These advanced entities reshape industries, automate complex tasks, and introduce a new paradigm of intelligent automation. This article will define AI agents, explain their operational mechanics, survey the top development platforms, illustrate their widespread applications, and provide comprehensive strategies for effectively monitoring and managing these powerful systems to ensure reliability and ethical deployment.
The Rise of AI Agents and LLMs: Why 2025 is a Pivotal Year
The landscape of artificial intelligence is experiencing an unprecedented acceleration, with 2025 emerging as a breakout year for AI agents and LLMs. These technologies are transitioning from experimental concepts to practical, impactful solutions across various sectors.
Investors, including those at Y Combinator, are keenly observing the rise of “vertical AI agents,” specialized systems designed to tackle specific, complex business challenges. These agents promise to embed intelligence directly into workflows, transforming how SaaS companies deliver value.
The rapid advancement in generative AI capabilities, combined with increasing computational power, enables LLMs to serve as the “brains” for these autonomous entities, allowing them to perceive, reason, plan, and act with unprecedented sophistication. This evolution signifies a pivotal shift from simple AI tools to intelligent, self-directed systems capable of driving significant operational efficiencies and competitive advantages.
What Exactly Are AI Agents?
An AI agent represents a leap beyond conventional software. At its core, an AI agent is an autonomous system designed to perceive its environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals. These agents operate with a degree of independence, distinguishing them from simpler, rule-based programs.
Key characteristics define AI agents:
- Perception allows them to gather information from their environment, whether through sensors, data streams, or user inputs.
- Memory enables them to retain past experiences and learnings, informing future decisions.
- Reasoning equips them to process information, evaluate options, and formulate plans.
- Action allows them to interact with their environment, executing tasks and influencing outcomes.
Distinguishing AI Agents from Bots and AI Assistants
Understanding the nuances between AI agents, bots, and assistants is crucial for appreciating their respective capabilities and suitable use cases. While these terms are sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct levels of intelligence and autonomy.
- Simple bots typically follow predefined rules or scripts, executing repetitive tasks and responding to specific commands with limited learning.
- AI assistants offer more advanced natural language processing, handling a broader range of commands, integrating with services, and sometimes learning user preferences. However, they generally require explicit commands within a bounded framework.
- AI agents, conversely, exhibit higher autonomy and intelligence. They can independently set goals, plan multi-step actions, adapt to unforeseen circumstances, and self-correct based on feedback.
How AI Agents and LLMs Work: The Cognitive Loop
The operational prowess of AI agents stems from a sophisticated “cognitive loop,” a continuous cycle of perception, memory, reasoning, and action. This architecture allows AI agents to exhibit adaptive and intelligent behavior, with Large Language Models (LLMs) playing a central role in driving their decision-making and execution.
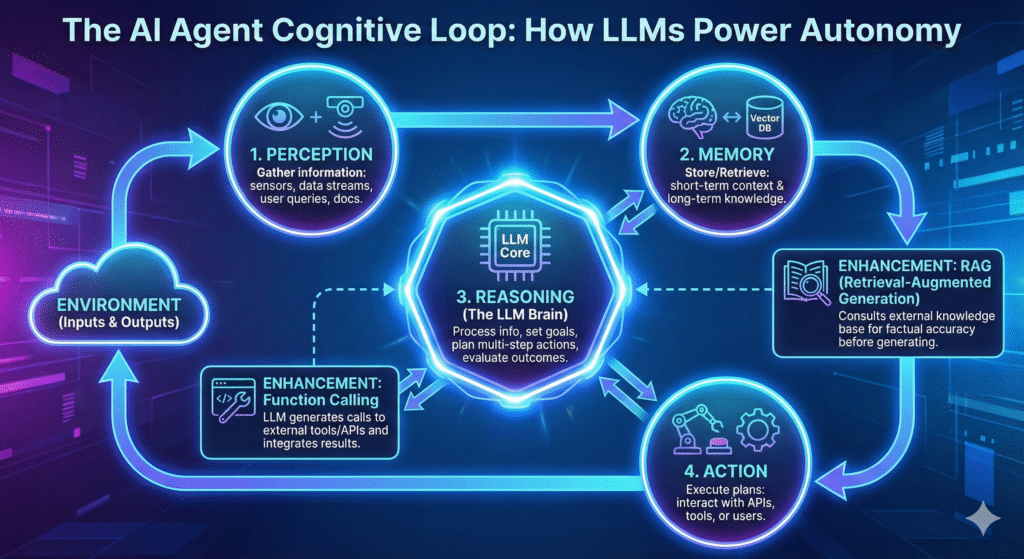
Perception
The agent gathers information from its environment—reading documents, processing sensor data, monitoring logs, or interpreting user queries. This perceived data is then fed into the Memory module.
Memory
The Memory module stores relevant information—both short-term context and long-term knowledge. It often uses a vector database for efficient semantic search and retrieval of past experiences or learned facts.
Reasoning
The LLM processes the perceived information and retrieved memories, performing tasks such as goal setting, planning multi-step actions, evaluating outcomes, and generating responses. It translates high-level objectives into actionable steps.
Action
The Action module executes the LLM’s planned steps—interacting with external tools, APIs, or human users. This output influences the environment, which is then perceived by the agent, restarting the loop.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG enhances LLM performance by retrieving factual information from an external knowledge base before generating a response, mitigating hallucination and ensuring accuracy.
Function Calling
LLMs can interact with external tools by generating structured calls to functions (e.g., web search, database query). The results are incorporated back into the agent’s reasoning process.
Key Applications and Use Cases of AI Agents Across Industries in 2025
AI agents are rapidly moving beyond theoretical discussions to become indispensable tools across a myriad of industries. In 2025, their ability to automate, personalize, and optimize processes is transforming operations and creating new value propositions worldwide.
Customer Service
From basic chatbots to proactive problem-solvers, agents handle complex inquiries, offer personalized recommendations, manage appointments, and anticipate customer needs.
Enterprise AI & Workflow Automation
Automating repetitive tasks—supply chain management, invoice processing, onboarding—while integrating with ERP and CRM systems.
Specialized Business Tasks
Market research, data synthesis, report generation: agents scour datasets, identify trends, summarize findings for actionable insights.
Healthcare
Administrative tasks, patient scheduling, preliminary diagnostic support, freeing professionals for critical roles.
E-commerce
Personalization, inventory management, dynamic pricing based on real-time demand and competitor analysis.
Top Platforms and Frameworks for Building AI Agents
1. Lyzr AI: Low-Code and Agentic Approach
Lyzr AI is a low-code framework engineered for building sophisticated generative AI applications. Its agentic approach allows creation of powerful AI agents with minimal coding.
- Integrated RAG pipelines ensure access to up-to-date, factual information from private or proprietary data sources.
- Local deployment options provide enhanced data privacy and security.
- Custom AI agent development tailored to specific business needs.
2. LangChain: The Versatile Framework for LLM Applications
LangChain allows developers to chain components—LLMs, prompts, parsers, tools—to create complex workflows. It offers memory management and community support for connecting agents to diverse data sources and APIs.
3. Other Notable Frameworks and Libraries (e.g., AutoGen, AutoGPT)
- AutoGPT: Autonomously pursues goals by breaking them into sub-tasks, leveraging LLMs for decision-making.
- AutoGen: Enables multi-agent systems where agents collaborate to solve tasks—communicating, debating, and strategizing.
Strategies for Monitoring and Managing AI Agents and LLMs Effectively
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for AI Agent Success
- Task completion rates
- Response times
- Decision accuracy
- Resource utilization
- Rate of successful tool calls
Ensuring Data Privacy and Security in Agent Deployments
Adopt privacy-by-design, data governance policies, access controls, secure infrastructure, and local deployment options to protect sensitive data.
Troubleshooting, Adapting, and Iterating AI Agent Behavior
- Error handling mechanisms for graceful recovery or escalation.
- Comprehensive logging and observability tools.
- Feedback loops: fine-tune prompts, update knowledge bases, refine logic.
Current Challenges and Future Limitations in AI Agent Development and Deployment
- Hallucinations & incorrect information generation.
- Scalability issues due to computational intensity.
- Complexity of debugging emergent behaviors.
- Ethical dilemmas: accountability, bias, transparency.
- Resource intensity limiting widespread adoption.
Getting Started: Choosing the Right AI Agent Approach for Your Needs
Begin by defining the problem you aim to solve. Consider technical capabilities, data privacy requirements, scalability needs, and community support versus vendor assistance. Start with a pilot project, iterate, and scale.
FAQs
- What infrastructure is needed for AI agents?
Cloud computing resources, vector databases, LLM APIs, monitoring tools. - Best platforms for building AI agents?
Lyzr AI (low-code), LangChain (modular), AutoGPT/AutoGen (open-source). - Where to find examples of AI agents or resources on them?
Platform websites, GitHub repositories, academic papers, AI community blogs. - Key trends for AI agents in 2025?
Increased autonomy, specialized vertical agents, multi-agent collaboration, improved RAG, focus on ethics and privacy. - How to choose the best platform?
Consider technical expertise, customization needs, integration ease, data privacy, task criticality. - Business applications in 2025?
Workflow automation, customer support, advanced data analysis, operational efficiencies, intelligent assistants. - What is a multi-agent AI framework?
System enabling multiple agents to collaborate on complex goals. - Open-source AI agent frameworks available?
LangChain, AutoGPT, AutoGen.
The Autonomous Future: Effectively Monitoring and Managing AI Agents
AI agents promise unprecedented efficiency and innovation across industries. Success hinges on understanding their mechanisms (cognitive loop, RAG), choosing the right development platform, and implementing robust monitoring, KPIs, data governance, and continuous improvement.
By prioritizing performance, security, and ethical considerations, organizations can navigate the complexities of this autonomous future, ensuring AI agents drive sustained innovation and deliver tangible value.